User Guide
PlanIT is a task managing application made specially for NUS computing students. PlanIT gives you the confidence that your busy schedule is organized and accounted for. Quickly and efficiently make and edit various tasks, mark dates, take note of remaining tasks, and more.
PlanIT also includes a calendar and a countdown feature to better manage your deadlines. It is even optimised for people who prefer typing, so that bookkeeping can be done faster. Now you can make progress on the things that are more important to you.
Objective:
PlanIT’s objective is to improve productivity for students with features and tools to help students manage their workload. These features significantly reduce the trouble of having to keep track of tasks, especially those that are essential yet repetitive. Features such as recurring schedule and date allow students to keep track of weekly tasks and due dates for tutorial homework, projects and much more. More importantly, the functionalities of PlanIt’s simple overview allows students to see upcoming deadlines or events.
Let’s dive deeper into these features to see how these features can assist students in workload management.
- Quick start
- How to use this guide
-
Features
- Glossary of attributes
- Constraints
-
List of Commands
- View Commands :
help—– Max - Making a task:
mk—– Jun Xue - Editing a task :
edit—– Han Bin - Postpone a task’s date :
snooze—– Max - Marking a task as done:
done—– Max - Listing all tasks :
ls—– Kai Xiang - Listing all uncompleted tasks :
ls not done—– Kai Xiang - Sort task by date:
sort by aorsort by d—– Han Bin - Searching a task by title:
find—– Kai Xiang - Searching a task by description:
find d/—– Kai Xiang - Searching a task by tag:
find t/—– Kai Xiang - Removing a task :
rmt—– Chloe - Removing a field from a task :
rmf—– Chloe - Counting down to a task :
count—– Chloe - Displaying statistics :
stat—– Chloe - View tasks on a date :
view—– Jun Xue - Clearing all entries :
clear - Exiting the program :
exit
- View Commands :
- Saving the data
- Editing the data file
- Calendar Specifications —– Jun Xue
- FAQ
- Command summary —– Kai Xiang, Max, Jun Xue, Chloe, HanBin
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your Computer. -
Download the latest
planit.jarfrom here. -
Copy the file to the folder you want to use as the home folder for your planner.
-
Double-click the file to start the app. The Graphical User Interface (GUI) similar to the below illustration should appear in a few seconds.
Note how the app contains some sample data.
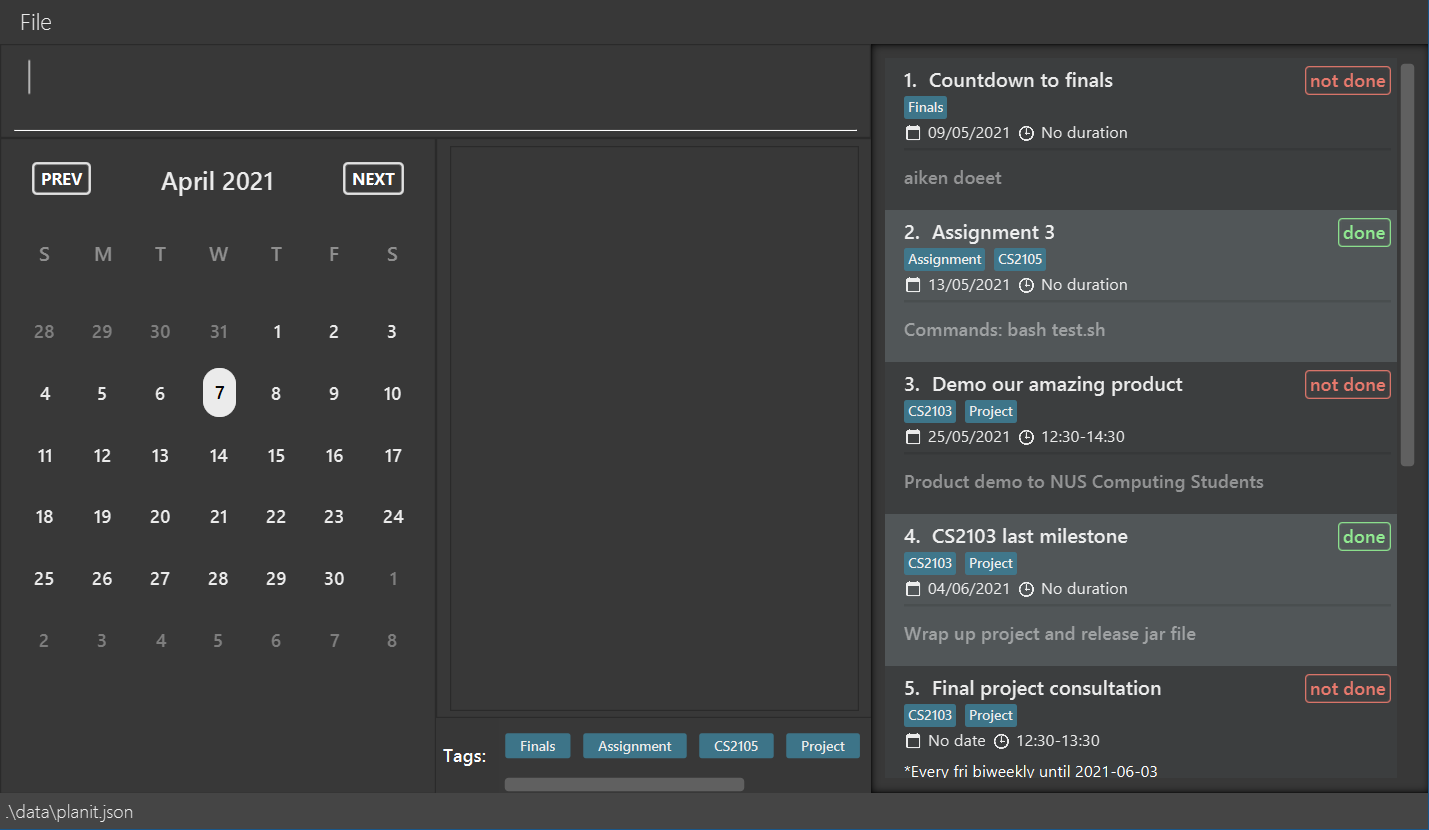
Here is a layout guide to the app.
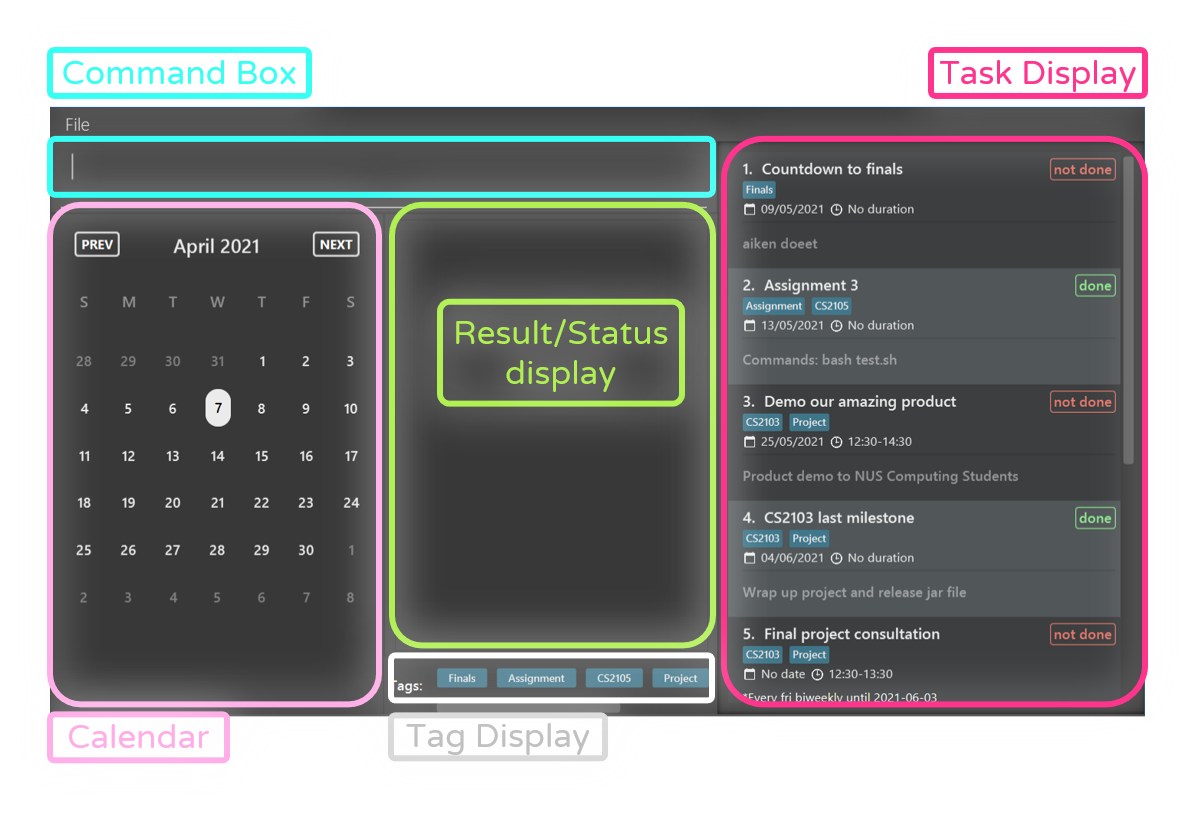
- Command Box : This is where you can enter the relevant commands in PlanIT.
- Result/ Status display : This displays feedback and useful information after you have entered the commands.
- Calendar : This displays the current dates and future dates for you to easily plan your tasks ahead of time.
- Tag Display : This shows all the available tags that the tasks have been categorised within PlanIT.
- Task Display : This shows all the tasks currently saved within the PlanIT app.
-
Type the command in the command box and press Enter to execute it. e.g. typing
helpand pressing Enter will display a list of commonly used commands for first time users.
Some example commands you can try:-
ls: Lists all tasks. -
mk n/eat dinner: Makes a task titledeat dinnerto the planner. -
rmt 3: Removes the 3rd task shown in the current planner.
-
-
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
How to use this guide
Here are some symbols you might need to know:
-
 : Helpful information you should take note of.
: Helpful information you should take note of. -
 : Useful tips that might help you.
: Useful tips that might help you. -
 : Important information that might affect your usage of PlanIT.
: Important information that might affect your usage of PlanIT.
Features
Glossary of attributes
PlanIT contains a list of tasks. Tasks can have the following attributes:
| Attribute | Prefix | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Title | n/ |
A short description or name for the task.
|
| Date | set/ |
A date to represent the deadline of a task or to represent the day that the task will be carried out.
|
| Duration | s/ |
The start and end time of a task. You should specify start time and end time in the 24-hour clock format.
|
| Recurring Schedule | r/ |
Represents a task that might repeat weekly or biweekly. e.g [23/10/2021][mon][weekly]
Suppose today is 06/04/2021 which falls on a Tuesday, user enters [30/06/2021][tue][weekly] for the recurring schedule field. The date of 06/04/2021 will not be included in the recurring dates and only recurring dates from the following tuesday will be included up till 30th June 2021 on a weekly basis. |
| Description | d/ |
A text description of the task. Your description can be any value.
|
| Tag | t/ |
A label attached to a task for easy grouping and searching of tasks. Your tag should only contain alphanumeric values.
|
| Status | st/ |
Reflects the current status of your task. Status can only be either ‘done’ or ‘not done’.
|
Constraints
In order to maximise the efficiency of adding tasks and ensuring that there are no unnecessary attributes, there are two constraints to the attributes that can exist on the tasks that you create or edit.
- Tasks cannot have Date and Recurring Schedule at the same time.
- Tasks cannot have Duration on its own without a Date or Recurring Schedule.
When it comes to Dates and Recurring Schedules, the main purpose of a Date attribute is to give a task a deadline or a single day to carry out the task itself. This should not co-exist with a Recurring Schedule, which can also indicate a task’s deadline or day to carry out the event, except it is being repeated on a weekly or biweekly basis.
As for the Duration of a task, it will be confusing to you as a user when you have multiple tasks with durations but no date specified. As such, this might cause you to miss your task or lower the efficiency of utilizing PlanIT when searching for tasks.
List of Commands
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user. Type in the prefixes along with the parameters.
e.g. inmk n/TITLE,n/TITLEis a parameter which can be used asn/eat dinner. -
Some commands might not require prefixes as written in their formats.
e.g. inrmt INDEX, it can be used asrmt 4. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/TITLE [t/TAG]can be used asn/Join Dance t/leisureor asn/Join Dance. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used as -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/TITLE set/DATE,set/DATE n/TITLEis also acceptable. -
If a parameter is expected only once in the command but you specified it multiple times, only the last occurrence of the parameter will be taken.
e.g. if you specifyn/first task n/second task, onlyn/second taskwill be taken. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp.
View Commands : help —– Max
Displays a list of commonly used possible commands along with each of their formats respectively so that you can refer to commands conveniently whenever you forget about them.
- Only a few main commands will be displayed to avoid information overload for first-time and forgetful users.
- Users can read the User Guide for detailed information on all the commands.
Format: help
Making a task: mk —– Jun Xue
Adds a task to the planner.
Tasks with the same title cannot be added to the planner
so that you do not have to worry about adding duplicate tasks by accident. Calendar will be reset.
Format: mk n/TITLE [set/DATE] [s/DURATION] [d/DESCRIPTION]
[r/RECURRING SCHEDULE] [st/STATUS] [t/TAG]…
- Only title is compulsory.
- Date should be in the format dd/mm/yyyy. For example, 1 July 2021
should be expressed as
01/07/2021, not 1/7/2021. - Duration should be numeric, contain 2 timings, and should be in 24 hours format with a colon, like
22:30-22:45. Duration can only exist when there is date or recurring schedule. - Description can have multiple lines by adding a line break using shift+enter.
- Recurring schedule should have 3 conditions which consist of:
- An end date when the task stops recurring.
- A day of the week that the task recurs on.
- Frequency of the recurring task.
- E.g.
[23/10/2021][Mon][weekly]
- Status can only be
doneornot done, and is by defaultnot done.
Examples:
-
mk n/eat dinner
Makes a task titled ‘eat dinner’. -
mk n/do project r/[29/06/2021][thu][Biweekly]
Makes a task titled ‘do project’ and will generate recurring dates that is on thursday, biweekly until 29th Jun 2021. Only the upcoming 3 recurring dates will be shown on the task display: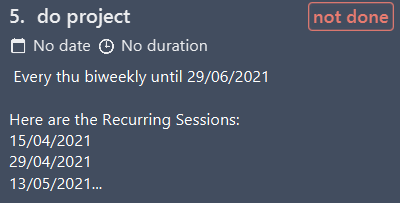
Example of making a task with multiple lines of description:
mk n/take a break d/
- do 1
- do 2 t/trying
Editing a task : edit —– Han Bin
Edits an existing task in the planner so that you can have the flexibility in making changes to a certain task if there is a change in your task or schedule. Calendar will be reset.
Format: edit INDEX [n/TITLE] [set/DATE] [s/DURATION] [d/DESCRIPTION]
[r/RECURRING SCHEDULE] [st/STATUS] [t/TAG]…
- Edits the task at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed task list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the task will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
Examples:
-
edit 1 set/10/10/2021 d/Remember to update User GuideEdits the date and description of the 1st task to be10/10/2021andRemember to update User Guiderespectively. -
edit 2 n/Buy textbook t/ set/Edits the title of the 2nd task to beBuy textbook.
Postpone a task’s date : snooze —– Max
Postpones your task’s date by a specified number of days so that you have the flexibility to push back the deadline of task when necessary.
Format: snooze INDEX [DAYS]
- Edits the task at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed list. The index must be a positive integer e.g 1, 2, 3, … -
DAYSmust be a positive integer and at most 365 (1 year). - The
DAYSis optional and it’s default value will be 1 if no number is specified in your command. - The snooze command will only successfully update the date of the task if the task contains a date.
Examples:
-
snooze 2Postpones the date of the task at index 2 in the list by 1 day. -
snooze 3 4Postpones the date of the task at index 3 in the list by 4 days.
Marking a task as done: done —– Max
Sets a task’s status to ‘done’ so that you can track the tasks that have completed easily.
Format: done INDEX
- Sets the task at the specified
INDEXto be done. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed list. - If the task’s status is already ‘done’, the planner will give a warning.
Example:
-
done 2Sets the status of a task at index 2 in the list to be done.
Listing all tasks : ls —– Kai Xiang
Shows a list of all tasks in the planner so that you can view all the tasks easily in one place. Calendar will be reset.
Format: ls
Listing all uncompleted tasks : ls not done —– Kai Xiang
Shows a list of all uncompleted tasks in the planner so that you can view all the uncompleted tasks easily. Calendar will be reset.
Format: ls not done
Note: The keyword not done is case-insensitive.
Sort task by date: sort by a or sort by d —– Han Bin
Sort tasks in the displayed list either in ascending dates or descending dates so that users would be able to see the task or event nearest to current date or furthest away from current date.
Format: sort by a or sort by d
- Sorts the displayed list. If
findcommand is used before sorting,sort by aorsort by dwill sort the displayed list only. To sort the entire list, make sure to uselsbefore sorting. - If
sort by a, task with no dates would appear last, subsequently task will be ordered in increasing dates. - If
sort by d, task with no dates would appear first, subsequently task will be ordered in decreasing dates. - If two tasks have the same dates, they will be ordered in equal priority.
Searching a task by title: find —– Kai Xiang
Find matching tasks based on the title keyword(s) provided so that you can find matching tasks quickly when only certain words from the title of the task can be remembered. Calendar will be reset.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
projectwill matchProject - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
CS2103 Projectwill matchProject CS2103 - Only full keywords will be matched. e.g.
projwill not matchprojects - No prefix (i.e.
t/,d/) should be in the search task by title query.
Examples:
-
find CS2103 team projectreturns matching tasks with title of following wordsCS2103,team,project
Searching a task by description: find d/ —– Kai Xiang
Find matching tasks based on the description keywords provided so that you can find matching tasks quickly when only certain words from the multi-line description can be remembered. Calendar will be reset.
Format: find d/KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
projectwill matchProject - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
CS2103 Projectwill matchProject CS2103 - Only full keywords will be matched. e.g.
projwill not matchprojects - Only a single
d/description prefix should be allowed. - No
t/tag prefix should be in the search task by description query. - No whitespace should be allowed right after the
find d/command likefind d/but will be allowed between the keywords in the command likefind d/Project CS2103.
Examples:
-
find d/write user guidereturns matching tasks with description of following wordsuser,guide,write
Searching a task by tag: find t/ —– Kai Xiang
Find matching tasks based on the tag keyword provided so that you can find matching tasks from the same category quickly when only the tag(s) can be remembered. Calendar will be reset.
Format: find t/KEYWORD
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
cs2103twill matchCS2103T - Only full keyword will be matched. e.g.
cs2103will not matchcs2103t - No
d/description prefix should be in the search by tag query. - Multiple
t/tag prefixes are allowed in the search task by tag query. - For each tag, the keyword must be single, alphanumeric unless searching task by keyword from multiple tags.
e.g.
projectCS2103will be a single tag keyword andproject CS2103will be recognised as keywords for 2 tags. - No whitespace should be allowed right after the
find t/command likefind t/but will be allowed between the keywords in the command likefind t/Project CS2103. - Suppose a task with multiple tags of
cs2103andcs2105, it will be returned as a matching task if the user inputs falls under the following cases:-
find t/cs2103only -
find t/cs2105only find t/cs2103 t/cs2105find t/cs2103 cs2105
-
![]() Suppose you want to find a task with multiple tags of
Suppose you want to find a task with multiple tags of cs2103 and cs2105
but entered find t/cs2103 Project, the task you want will not be found since it will be detected
as a find a task by tag with cs2103 and Project.
So, it is best to be more general than specific here by putting lesser tag keywords when unsure.
Examples:
-
find t/CS2103returns matching tasks with tag ofCS2103orcs2103 - Below is an illustration of how to search matching tasks based on multiple tags:
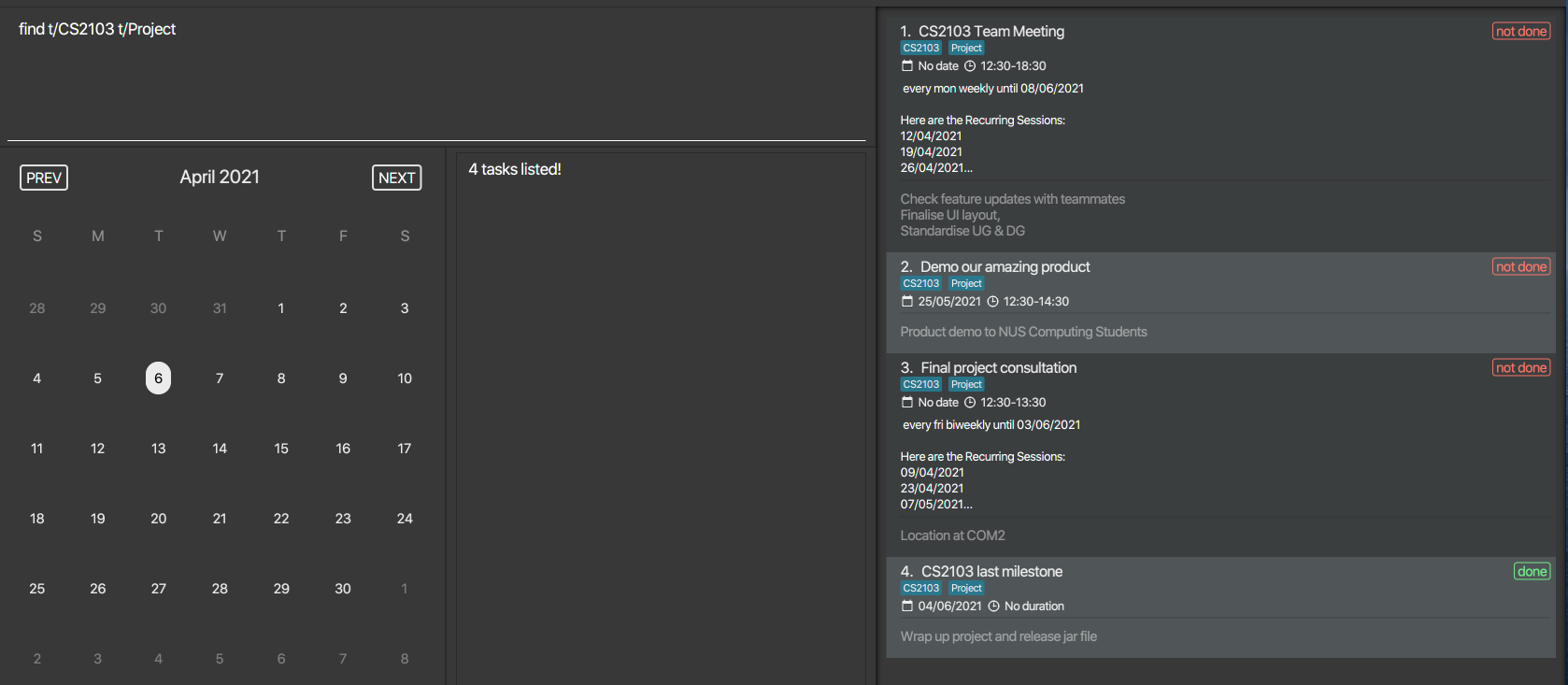
![]() It is optional to keep putting tag prefix
It is optional to keep putting tag prefixt/ for searching task with multiple tags
Removing a task : rmt —– Chloe
Removes an existing task from the planner so that you can reduce clutter from the planner or remove a mistakenly added task easily.
Format: rmt INDEX
- Removes the task at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed planner.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
lsfollowed byrmt 2removes the 2nd task in the planner. -
find Workfollowed byrmt 1removes the 1st task in the result of thefindcommand.
Removing a field from a task : rmf —– Chloe
Removes an existing field from a task in the planner so that you can remove certain details from the task directly without having to go through the hassle of removing the task and adding the same task with lesser fields again.
Format: rmf INDEX FIELD
- Removes the specified field of task at
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed planner.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
- Fields are specified in the format their respective attributes:
set/,s/,r/,d/,t/. - Exactly one field must be specified.
- Title and status fields cannot be removed.
Examples:
-
lsfollowed byrmf 2 d/removes the description from the 2nd task in the planner. -
find Catfollowed byrmf 1 t/removes all the tags from the 1st task in the result of thefindcommand.
Counting down to a task : count —– Chloe
Displays the number of days left to a task’s date if it exists so that you know how much time you have left to work on the task.
Format: count INDEX
- Counts the number of days until the date of the task at
INDEX. - Number of days is solely dependent on the system date only irrespective of system timing e.g if the current date is 12/05/2021 and the task has date 13/05/2021, the result displayed will be 1.
- The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed planner.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
- The task at the index must have a date, otherwise countdown cannot be done.
Examples:
-
lsfollowed bycount 4displays the number of days left to the 4th task in the planner. -
find Woolfollowed bycount 1displays the number of days left to the 1st task in the result of thefindcommand.
Displaying statistics : stat —– Chloe
Displays the statistics of the planner so that you can check the current task progression and determine your own work efficiency conveniently.
Statistics include:
1) The total number of tasks in the planner.
2) The percentage of tasks completed (marked as done).
3) The number of tasks due in the next 7 days from the system’s current time.
Format: stat
- Planner must consist of at least one task.
Examples:
-
lsfollowed bystatdisplays the statistics for all the tasks in the planner. -
find cs2103followed bystatdisplays the statistics for all the tasks withcs2103in their title.
View tasks on a date : view —– Jun Xue
Displays the tasks happening on a particular date, including recurring tasks, and brings the calendar to the date specified so that you may find free time on the day to schedule new activities.
Format: view DATE
- Date should be in the format of dd/mm/yyyy like 12/12/2021.
- Date cannot be before the year 1900 or after the year 2099.
Examples:
-
view 03/07/2021
Lists all tasks with dates or recurring dates on 03/07/2021, and brings the calendar to July 2021.
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the planner so that you can remove all tasks within the planner at once. Calendar will be reset.
Format: clear
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
Saving the data
PlanIT data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Editing the data file
PlanIT data are saved as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/planit.json.
Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Calendar Specifications —– Jun Xue
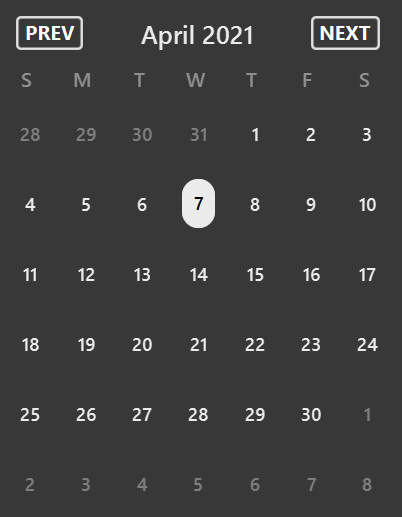
You can click on the prev and next buttons on the calendar shown above, to move to the previous and next months respectively,
or you can simply type in the following commands, if you are more inclined to using the command line interface.
| Action | Format |
|---|---|
| Navigate to the previous month on the calendar | prev |
| Navigate to the next month on the calendar | next |
-
These 2 commands do not take in parameters. Extraneous parameters will be ignored.
E.g. if the command specifies
prev 987, it will be interpreted asprev. -
nextandprevoperates on the currently displayed month. - The displayed date and month will revert to the current date and month upon starting up the app.
- Month displayed can go beyond
datelimits.
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file
that contains the data of your previous PlanIT home folder.
Q: Does PlanIT requires an Internet connection for the app to run?
A: PlanIT does not require Internet connection and can run locally on your computer.
Q: How do I remove my data without starting up the PlanIT app?
A: Delete the data folder from the PlanIT home folder.
Q: How do I backup my data in PlanIT app?
A: Copy the data folder from PlanIT and saved it in a external hard disk. cloud storage such as Google Drive
or to the internal hard disk of your computer.
Command summary —– Kai Xiang, Max, Jun Xue, Chloe, HanBin
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Make |
mk n/TITLE [set/DATE] [s/DURATION] [d/DESCRIPTION] [r/RECURRING SCHEDULE] [st/STATUS] [t/TAG]…e.g., mk n/eat dinner t/important
|
| Clear | clear |
| Mark Done | done INDEX |
| Remove Task |
rmt INDEXe.g., rmt 3
|
| Remove Field |
rmf INDEX FIELDe.g., rmf 1 d/
|
| Postpone | snooze INDEX [DAYS] |
| Edit |
edit INDEX [n/TITLE] [set/DATE] [s/DURATION] [d/DESCRIPTION] [r/RECURRING SCHEDULE] [st/STATUS] [t/TAG]…e.g., edit 2 n/James Lee
|
| Find |
find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., find CS2103 team project find [t/TAG] e.g., find t/CS2103 find [d/DESCRIPTION] e.g., find d/CS2103 milestone postmortem
|
| Countdown |
count INDEX e.g., count 2
|
| Statistics | stat |
| View |
view DATEe.g., view 10/10/2021
|
| List |
lsls not done
|
| Help | help |
| Calendar Navigation |
next prev
|